
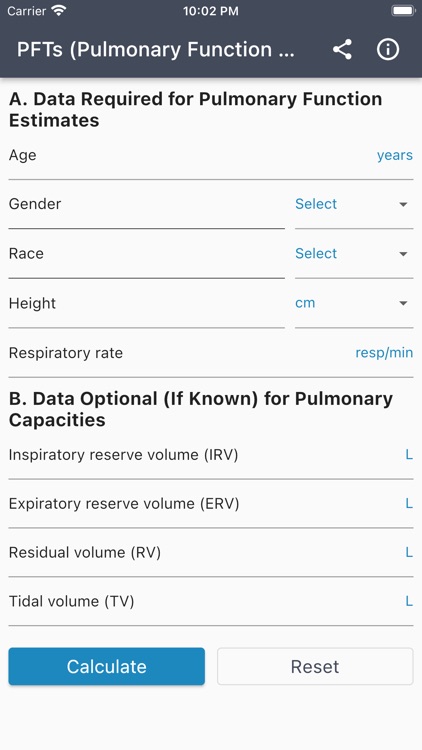
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) evaluate the respiratory function, essentially how well the lungs are working

Pulmonary Function Tests PFTs


What is it about?
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) evaluate the respiratory function, essentially how well the lungs are working.

App Screenshots




App Store Description
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) evaluate the respiratory function, essentially how well the lungs are working.
Disclaimer: Always seek a doctor’s advice in addition to using this app and before making any medical decisions. This app should NOT be considered as a substitute for professional medical service, NOR as a substitute for clinical judgement.
This spirometry calculator app uses the following equations.
Tidal Volume (TV)
Tidal volume is the measure of the amount of air inhaled during a normal breath. Safe tidal volumes can be determined based on patient’s height and gender and the rule of thumb of 6 to 8mL per kg of ideal body weight (IBW) where:
IBW male = 50kg + 2.3 x (Height in inches – 60)
IBW female = 45.5kg + 2.3 x (Height in inches – 60)
Normal range for measured tidal volume is 500 – 780 mL.
Minute Volume (VE)
Minute ventilation or minute volume, is defined as the total volume of gas entering (or leaving) the lung per minute and is calculated as product of tidal volume and respiratory rate.
VE in mL/min = Tidal volume (Vt) in mL x Respiratory rate (RR) in resp/min
Normal range for minute volume is 70 – 110 mL/kg/min or in average adults (4.0 – 8.0 L/min).
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
The peak expiratory flow rate predicts the maximum speed of expiration and offers information about the airflow through the bronchi, thus can quantify how severe the degree of airway obstruction is.
Peak expiratory flow is estimated via one of the three formulas, depending on the patient characteristics:
Children PEFR = ((Height in cm - 100) x 5) + 100
Adult Men = (((Height in m x 5.48) + 1.58) - (Age x 0.041)) x 60
Adult Women = (((Height in m x 3.72) + 2.24) - (Age x 0.03)) x 60
Normal range in adults is between 390 and 740 L/min.
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC)
Forced vital capacity (FVC) is the total amount of air exhaled during the FEV test.
FVC = Race x 1.15 x [(0.0443 x Height) - (0.026 x Age) - 2.89]
Where Race variables are: 0.93 for Asian, 0.87 for Black or African American and 1 for White Caucasian.
Normal range FEV1 is between 3.0 and 5.0 L
Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV1)
Forced expiratory volume (FEV1) measures how much air a person can exhale during the first second of a forced breath.
FEV1 = Race x 1.08 x [(0.0395 x Height) - (0.025 x Age) - 2.6]
Where Race variables are: 0.93 for Asian, 0.87 for Black or African American and 1 for White Caucasian.
Normal range FEV1 is between 2.4 and 4.0 L. Lower FEV1 values are indicative of obstructive lung disease, such as asthma or COPD.
Estimated Vital Capacity
Vital capacity can be indirectly estimated based on gender, age and height in centimetres.
VC for men = [(27.63 – 0.112 x Age in years) x Height in cm] / 1000
VC for women = [(21.78 – 0.101 x Age in years) x Height in cm] / 1000
Subject age is taken into account as a factor because vital capacity increases during the 20s and 30s and then follows a steady decrease towards the 50s. The VC estimation is gender specific (men tend to have a higher volume than women) but the general normal range is between 3.0 and 5.0 L.
Pulmonary Capacities
During spirometry, the four respiratory volumes are measured: inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), tidal volume (TV), expiratory reserve volume (ERV) and residual volume (RV). These are then used to determine the lung capacities, defined as:
Lung Capacity Formula Normal Range
Vital Capacity (VC) IRV + TV + ERV 3.0 – 5.0 L
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) ERV + RV 2.0 – 4.0 L
Total Lung Capacity (TLC) IRV + TV + ERV + RV 4.0 – 6.0 L
AppAdvice does not own this application and only provides images and links contained in the iTunes Search API, to help our users find the best apps to download. If you are the developer of this app and would like your information removed, please send a request to takedown@appadvice.com and your information will be removed.