
Metabolic drug-drug interactions (DDIs) are a major concern in drug development

Simcyp Static DDI Calculator



What is it about?
Metabolic drug-drug interactions (DDIs) are a major concern in drug development. Early identification of DDI potential is critical to both investigating mitigations and future clinical trial design, and therefore predictions of DDIs are important to make quantitative estimates. Current assessment of DDI can be estimated by the ratio of the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) in comparison to the control state. Predictions of DDIs can be made from combining both in vitro and in vivo data and applied in a ‘static’ model, or alternatively more dynamically through application of a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic approach such as the Simcyp® population-based absorption, distribution metabolism and excretion (ADME) simulator.

App Screenshots




App Store Description
Metabolic drug-drug interactions (DDIs) are a major concern in drug development. Early identification of DDI potential is critical to both investigating mitigations and future clinical trial design, and therefore predictions of DDIs are important to make quantitative estimates. Current assessment of DDI can be estimated by the ratio of the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) in comparison to the control state. Predictions of DDIs can be made from combining both in vitro and in vivo data and applied in a ‘static’ model, or alternatively more dynamically through application of a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic approach such as the Simcyp® population-based absorption, distribution metabolism and excretion (ADME) simulator.
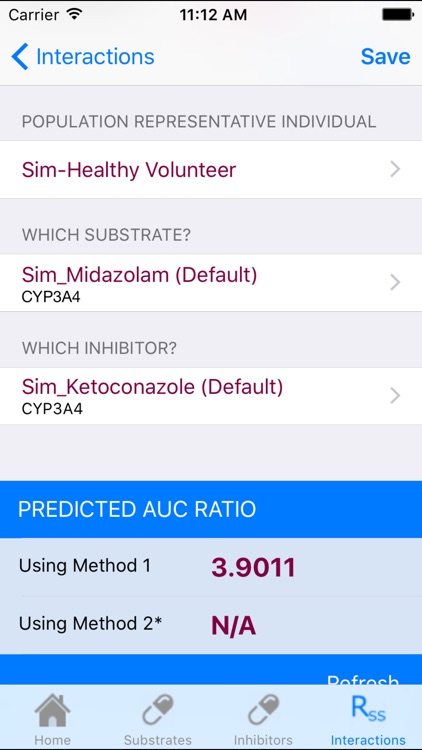
The Simcyp Static DDI Calculator is a standalone application which has been developed to allow the quick and accurate calculation of the predicted drug-drug interaction (DDI) risk in a population representative individual.
Once the substrate and inhibitor compounds have been compiled the user can rapidly calculate the DDI risk in a given population representative for the target compound. The risk of DDI can be predicted from the Rss value – the observed ratio of the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) following a dosing regimen of the inhibitor in comparison with the control incubation (i.e. no inhibitor). Two specific predicted AUC ratios are calculated:
Method 1: This uses the Simcyp equations and assumptions to generate the predicted AUC ratio.
Method 2: This uses the equations and assumptions listed in the 2012 FDA draft guidance (page 54) which is based on the published approach (Fahmi et al, 2008) to predict the AUC ratio.
Once a value for the AUC has been generated the clearance of a drug can be accurately calculated, independent of the profile of the generated concentration-time curve.
AppAdvice does not own this application and only provides images and links contained in the iTunes Search API, to help our users find the best apps to download. If you are the developer of this app and would like your information removed, please send a request to takedown@appadvice.com and your information will be removed.